Do you have pain around your knee? How do you know if the pain is coming from your knee or other structures in the area? Do you hear a click, a pop, feel like your knee is catching or going to give out? If not, it may not be the ligaments or meniscus in the knee that is causing your pain. It could be coming from other structures that surround your knee. A physiotherapist will be able to assess your knee to determine what is causing your pain.
What is the pes anserine?
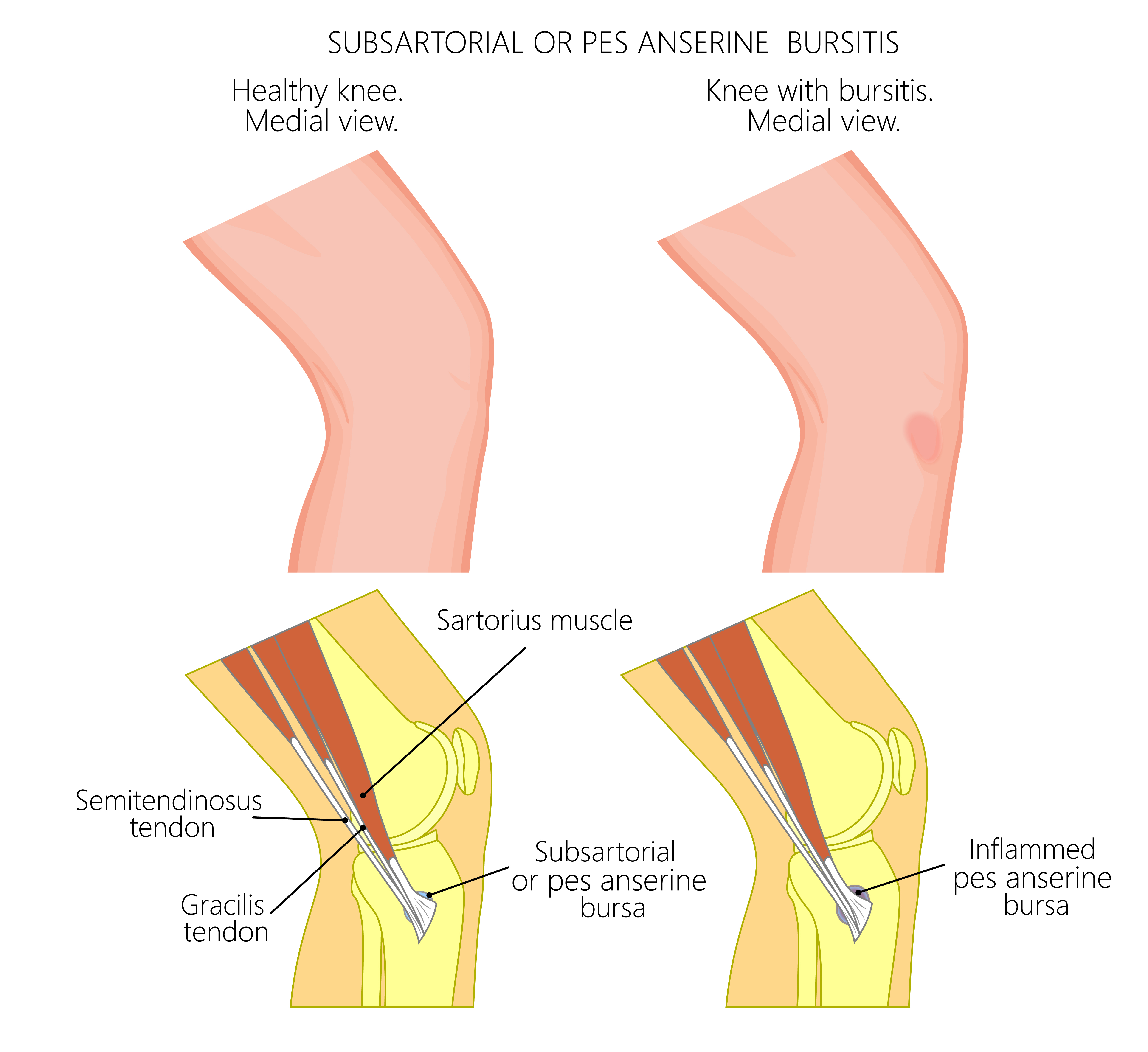
The pes anserine is a term used for the boney landmark where 3 muscles (sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus) attach onto the same location on the tibia bone on the inside of the leg below the knee. These muscles perform different actions but are primarily flexors of the knee.
What is bursitis?
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions to reduce friction between bones, muscles, and tendons. When this bursa becomes irritated and inflamed, it is called bursitis. It can become inflamed with repetitive overuse of the muscles or from direct trauma to the region of the bursa.
So, what is pes anserine bursitis?
The pes anserine bursa is located between the tibia bone and the tendons of the pes anserine muscles. This inflamed bursa can cause knee or lower leg pain and is called pes anserine bursitis.
Pes Anserine Bursitis Signs and Symptoms
- Pain and tenderness on the inside of the knee and upper shin
- Pain while running, using stairs, or in sports that involve kicking, squatting, quick movements side to side
- Possible swelling at the location of the bursa
- Decreased knee range of motion and muscle strength
- Gait abnormalities
Physiotherapy Assessment and Treatment
A physiotherapist will conduct a thorough history and physical examination to determine if you are presenting with pes anserine bursitis. Treatment can include multiple therapeutic modalities, manual therapy, and a comprehensive exercise program. Your physiotherapist may choose to incorporate ice, therapeutic ultrasound, stretching, and strengthening when appropriate. They may also educate you to avoid certain activities until bursitis has settled down.
It is important to have your injury evaluated by a physiotherapist so they can determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Medical Management
As this is an inflammatory condition, it could be appropriate to visit your family doctor who may prescribe an anti-inflammatory medication to help alleviate pain. In more severe cases when the condition is not alleviated with mediation and/or physiotherapy alone, your doctor may consider sending you for cortisone injections in conjunction with physiotherapy treatment.